WHAT IS JAW FRACTURE?
A jaw fracture happens when the jawbone, also known as the mandible, breaks. This can be due to accidents, sports injuries, fights, or falls. Jaw fractures can cause pain, difficulty eating or speaking, and swelling.



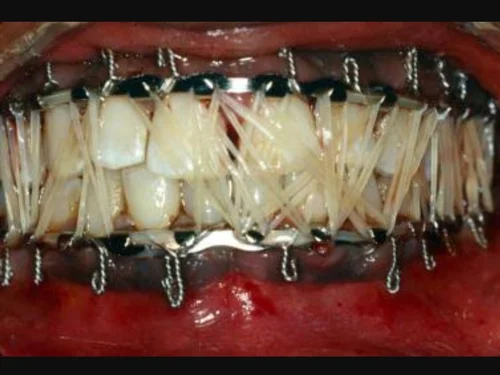

| TYPES OF JAW FRACTURES:
- Simple Fracture: This is when the jawbone breaks into two pieces but stays in place.
- Compound Fracture: In this type, the broken bone pierces the skin. It’s more severe and can lead to infections.
- Displaced Fracture: Here, the broken pieces of the jawbone move out of their normal position, causing misalignment.
| SYMPTOMS:
- Pain in the jaw or face.
- Difficulty opening the mouth.
- Swelling or bruising around the jaw.
- Problems with biting or chewing.
- Numbness in the lips or chin.
| TREATMENT:
- Medical Evaluation: A doctor will examine the jaw and may order X-rays or CT scans to determine the extent of the fracture.
- Immobilization: For minor fractures, the jaw may be immobilized using wires, rubber bands, or braces to keep it stable while it heals.
- Surgery: Severe fractures may require surgery to realign the bones and secure them with plates, screws, or wires.
- Pain Management: Pain medications may be prescribed to manage discomfort during the healing process.
- Dietary Changes: Soft or liquid diets may be recommended to prevent further injury while the jaw heals.
| CONCLUSION:
In conclusion, jaw fractures, whether simple or compound, can cause pain, difficulty with eating and speaking, and swelling. Treatment options range from immobilization with wires to surgery for severe cases, with a focus on pain management and dietary adjustments. Recovery time
FAQ
Most frequent questions and answers
Jaw fractures can result from various incidents, including car accidents, falls, sports injuries, physical altercations, or even medical conditions weakening the bones.
Common symptoms include pain, swelling, difficulty opening the mouth, misalignment of the jaw, bruising, numbness in the chin or lips, and problems with biting or chewing.
- Seek immediate medical attention. Refrain from moving the jaw excessively, apply ice packs to reduce swelling, and avoid eating or drinking until evaluated by a healthcare professional.
A doctor will conduct a physical examination, possibly followed by X-rays or CT scans to assess the extent and location of the fracture.
Treatment depends on the severity of the fracture. Options may include immobilization with wires, braces, or rubber bands; surgery to realign and stabilize the bones; pain management; and dietary modifications.


